Hall Effect in Metals
Order Code: 55548E
Category: Physics Trainers
Hall Effect enables the charge carrier concentration and mobility to be determined by experiment. Direction of the Hall Voltage in silver indicates negative charge carriers, which is in agreement with concepts of the model of the ‘free electron...
SPECIFICATION
Hall Effect enables the charge carrier concentration and mobility to be determined by experiment. Direction of the Hall Voltage in silver indicates negative charge carriers, which is in agreement with concepts of the model of the ‘free electron gas‘. Limitations of this model are shown by the so called ‘ abnormal Hall Effect’ of tungsten. The experiment carried out under identical conditions for tungsten show the Hall Voltage to have about same magnitude but opposite direction as in silver.
This can be explained by the ‘Energy Band diagram’. The tungsten atom has …….5s2 5p6 5d4 6s2 electronic structure.When the atoms come close together to form the solid, the close lying states 5d and 6s broaden into bands, with s band broadening considerably more than the d band. This is because of the larger size of the s orbital. The figure schematically shows the allowed energies as a function of the interatomic distance. The number of allowed states is ten per atom in the d band and two in the s band. In tungsten there are six electrons to be shared between these two bands. The result is that at the interatomic distance in tungsten there are holes in the d band and electrons in the s band, making tungsten predominantly a hole conductor.
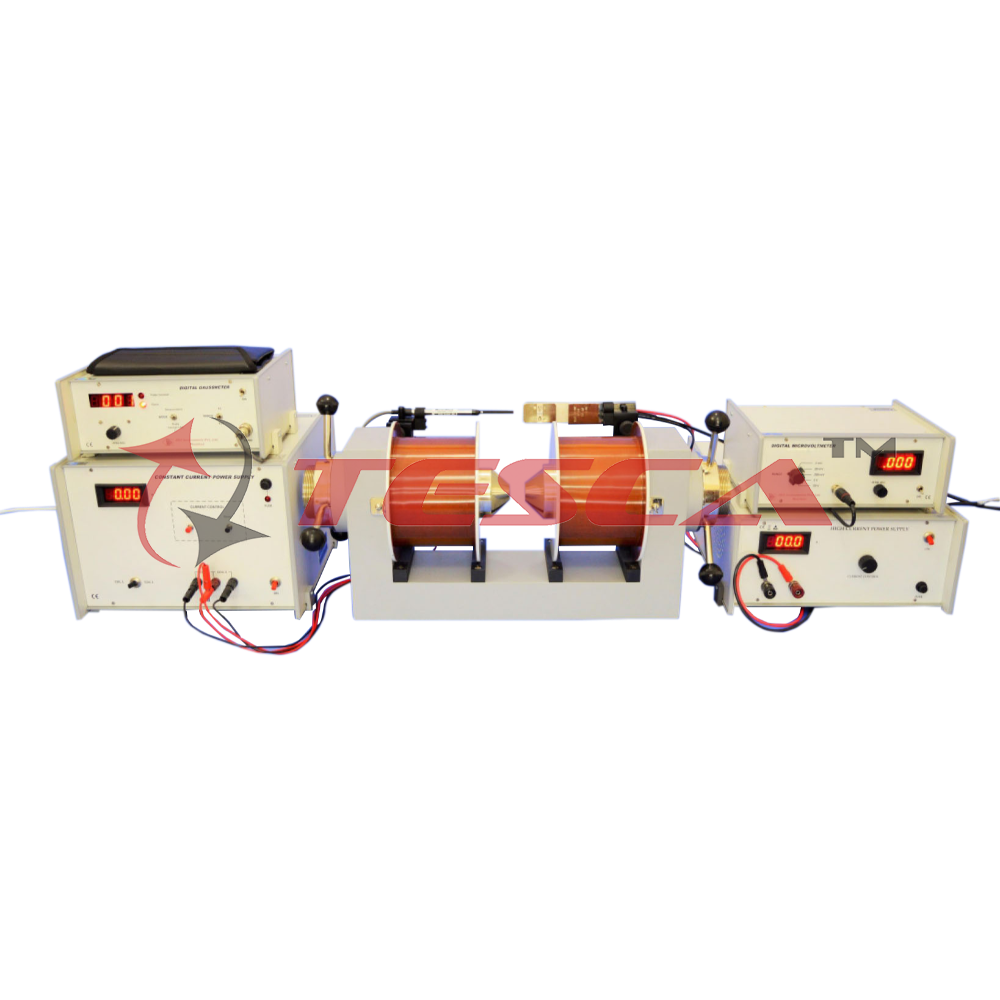
This sort of mixed (electrons and holes) conduction is a general characteristic of transition metals. The apparatus consists of the following:
a) Hall Probes-Silver(HP-Ag)
Technical Specification
- Material : Silver(8X6X0.05 mm)
- Contacts : Press Type for current
- Spring type for Voltage
- Hall Voltage : ~17 mV/10A/10KG
b) Hall Probe-Tungsten (HP-W)
Technical Specification
- Material : Tungten Strip (8 x 6 x 0.05 mm)
- Contacts : Press type for current
- Spring Type for Voltage
- Hall Voltage : ~15 mV/10A/10KG
c) High Current Power Supply
Technical Specification
- Range : 0-20A continuosly variable
- Accuracy : ±0.5%
- Regulation : ±0.5% for ±10% variation of mains
- Display : 3½ digit, 7 Segment LED
d) Digital Microvoltmeter
It is a very versatile multipurpose instrument for the measurement of low dc voltage. It has 5 decade ranges from 1mV to 10mv with 100% over-ranging. For better accuracy and convenience, readings are directly obtained on 31/2 digit DPM (Digital Panel Meter).
Technical Specifications
- Range : 1mV, 10mV, 100mV, 1V & 10V with 100% over-ranging.
- Resolution : 1μV
- Accuracy : ±0.2% ±1 digit
- Stability : Within ±1 digit
- Input Impedance : >1000MW (10MW on 10V range)
- Display : 3½ digit, 7 segment LED with autopolarity and decimal indication
e) Electromagnet
Technical Specification
- Pole Pieces : 75mm tappered to 25mm
- Mag. Field : 17KG ±5% at 10mm airgap
- Energising Coils : Two of approx. 13 each
- Power : 0-90Vdc, 3A, for coils in series 0-45Vdc, 6A, for coils in parallel
f) Constant Current Power Supply
g) Gaussmeter
The experiment is complete in all respect.










 91-9829132777
91-9829132777