Pressure and Temperature Module
Order Code: 25268461.6
Category: General Lab Equipment V
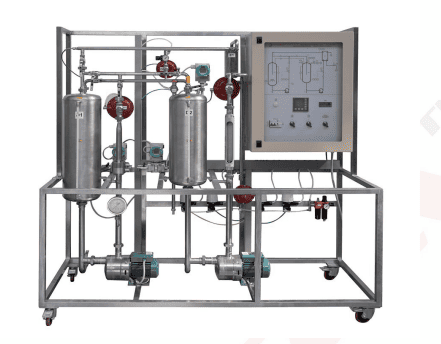
Key Features and Components Control and Monitoring System: PID Controller: A microprocessor-based PID controller that provides Proportional, Integral, and Derivative control. It includes a 4-line LCD display to visualize control ...
SPECIFICATION
Key Features and Components
-
Control and Monitoring System:
-
PID Controller: A microprocessor-based PID controller that provides Proportional, Integral, and Derivative control. It includes a 4-line LCD display to visualize control parameters and a serial card for PC connectivity.
-
SCADA Software: Enables real-time supervision and data acquisition through a Windows-compatible software interface. It allows the monitoring of ON-OFF control, analog PID signals, and both real-time and historical trends.
-
-
Physical Components:
-
Storage Tank: Constructed from AISI 304 stainless steel, with a 20-liter capacity for water storage. This tank plays a crucial role in controlling the water level and provides stability to the system.
-
Heating System: Includes a 3 kW electric heating element to control the temperature of the water, essential for studying thermal processes.
-
Heat Exchanger: A plate-type heat exchanger for controlling the heat transfer between two fluids, used for temperature regulation.
-
Centrifugal Pumps: Two pumps with a flow rate of 4 m³/h each, used for circulating water through the system and enabling flow rate control.
-
Pneumatic Control Valves: Four valves of varying flow coefficients (Cv = 2.5 and Cv = 0.32) control the flow and pressure within the system. These valves regulate the water flow and pressure based on PID control commands.
-
-
Measurement Instruments:
-
Flow Rate Measurement:
-
Differential-pressure transmitter for measuring flow rate, providing an output signal of 4 to 20 mA.
-
A variable-area flowmeter with a range of 0 to 1000 l/h for flow rate measurement.
-
-
Level Measurement:
-
An electronic differential-pressure transmitter measures the level with a range of 0 to 500 mm H2O.
-
-
Pressure Measurement:
-
An electronic transmitter of relative pressure with a range of 0 to 2 bar and a 4 to 20 mA output signal for accurate pressure measurement.
-
-
Temperature Measurement: A Pt100 thermo resistance is used for temperature sensing, ensuring accurate and stable temperature readings.
-
-
Piping and Valves:
-
The system is equipped with AISI 304 stainless steel piping and valves, ensuring durability and resistance to corrosion. The various control valves and transmitters are strategically placed for optimal control of the system.
-
Experimentation and Learning Objectives
This module offers a rich set of experiments that allow users to explore various control strategies and system behaviors, focusing on flow rate, level, temperature, and pressure control. Some of the key learning objectives include:
-
ON-OFF Control:
-
Understanding and analyzing the basic ON-OFF control strategy for simple control applications.
-
-
PID Control:
-
Experimenting with Proportional, Integral, and Derivative control strategies for fine-tuning and optimizing control in more complex systems.
-
-
Measuring Instruments:
-
Understanding how various instruments like differential-pressure transmitters, flowmeters, and temperature sensors are used to measure key process variables.
-
-
Determining Process Characteristics:
-
Learning how to determine system characteristics such as dead time and response time for various process variables, which are crucial for effective controller tuning.
-
-
Controller Tuning:
-
Experimenting with different PID tuning techniques to optimize the system's performance and response time. This includes methods like Ziegler-Nichols or trial-and-error tuning.
-
-
System Supervision:
-
Using the SCADA software to supervise and control the system. The software allows real-time control, visualizing trends, and analyzing historical data for process optimization.
-
Technical Specifications
-
Storage Tank: 20L capacity, made of AISI 304 stainless steel, designed for water storage.
-
Heating System: 3 kW electric heating element for temperature control.
-
Heat Exchanger: Plate-type exchanger used for thermal regulation.
-
Centrifugal Pumps: 2 pumps, each with a 4 m³/h capacity, for water circulation.
-
Control Valves:
-
2 pneumatic control valves with Cv = 2.5 for flow and pressure control.
-
2 pneumatic control valves with Cv = 0.32 for more precise adjustments.
-
-
Measurement Instruments:
-
Flow Rate: Differential-pressure transmitter (4-20 mA output) and variable-area flowmeter (0-1000 l/h range).
-
Level: Differential-pressure transmitter (0 to 500 mm H2O range, 4-20 mA output).
-
Pressure: Electronic pressure transmitter (0 to 2 bar, 4-20 mA output).
-
Temperature: Pt100 thermo-resistance for temperature measurement.
-
-
PID Controller: A microprocessor-based controller with LCD display and serial card for PC connection.
-
SCADA Software: Provides control and data acquisition, allowing for ON-OFF control, analog signal control, and real-time and historical trend monitoring.
System Components and Data Acquisition
-
The SCADA software enables users to monitor real-time data, observe trends, and analyze historical data for further optimization and troubleshooting of the system.
-
Users can control different process variables (flow rate, level, temperature, and pressure) and adjust PID parameters through the PID controller interface.
Summary of Use and Learning Goals
The Pressure and Temperature Module serves as an ideal training tool for understanding and experimenting with the principles of industrial process control. It provides a comprehensive learning platform for students or engineers to:
-
Explore multi-loop PID control for controlling several process variables simultaneously.
-
Study the effects of PID tuning on system performance.
-
Gain hands-on experience with industrial-grade instruments like differential-pressure transmitters, flowmeters, and temperature sensors.
-
Analyze system dynamics through real-time control and data acquisition using SCADA software.
-
Learn practical skills in flow, level, temperature, and pressure control, critical for many industrial applications such as chemical processing, HVAC systems, and energy management.
This module is particularly useful in educational settings or technical training centers, where learners can get familiar with both the theoretical and practical aspects of process control systems.








 91-9829132777
91-9829132777