Belt Drive Study Apparatus
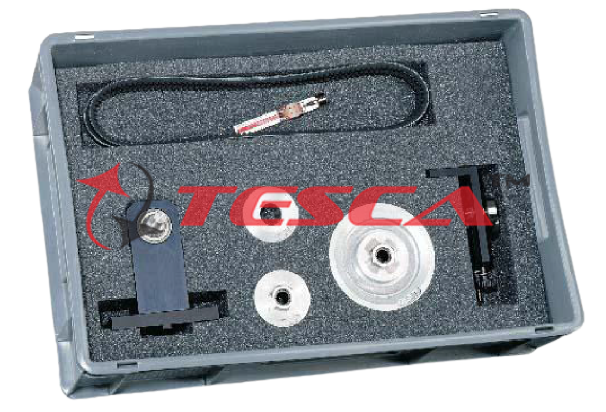

Order Code: 32218
Category: Strength of Materials Lab
Features The wastewater treatment plant on a laboratory scale Aerobic biological degradation of organic substances Nitrification and pre-de-nitrification Tesca Activated Sludge Process Apparatus is the most ...
SPECIFICATION
Features
- The wastewater treatment plant on a laboratory scale
- Aerobic biological degradation of organic substances
- Nitrification and pre-de-nitrification
Tesca Activated Sludge Process Apparatus is the most important biological process in water treatment. 32118 enables this process to be demonstrated.
A pump delivers raw water contaminated with dissolved organic substances (organic matter) into the aeration tank. Aerobic microorganisms (activated sludge) in the aeration tank use organic matter as a source of nutrition, biodegrading it in the process. Since aerobic microorganisms need oxygen, the raw water is aerated in the aeration tank. The activated sludge is mixed with the raw water by stirring machines. In the secondary clarifier, the activated sludge is then separated from the treated water by sedimentation. A portion of the activated sludge is returned to the aeration tank (return sludge). The treated water is collected in a tank.
It is also possible to convert ammonium into nitrate (nitrification) and nitrate into nitrogen (de-nitrification). For de-nitrification, a zone without aeration can be created in the aeration tank by installing a partition wall. The following flow rates are adjustable: raw water, return sludge, internal recirculation for pre-de nitrification, and air. Oxygen concentration, pH value, and temperature can be controlled. Optionally a software program can be provided to display the operation states and measure data. A process schematic shows the current operating states of the individual components and the measured data.
Samples can be taken at all relevant points. Activated sludge from a wastewater treatment plant and analysis technology is required for the experiments. Recommended parameters are:
- BOD5 (biochemical oxygen demand)
- COD (chemical oxygen demand)
- NH4 (ammonium)
- NO3 (nitrate)
Specifications
Biological wastewater treatment
Aeration tank with 3 stirring machines
Secondary clarifier
Nitrification and pre-de-nitrification
Separate supply unit with 2 stirring machines
All relevant flow rates adjustable
Control of temperature, pH value, and oxygen concentration
Measurement of flow rate, temperature, pH value, and oxygen concentration
Optional software for data acquisition via USB under Windows and display of the operation states & visual inspection with a webcam on PC
Technical Specifications
Aeration tank
? Capacity nitrification zone: approx. 34L
? Capacity de-nitrification zone: approx. 17L
Tanks
? Secondary clarifier: 30L
? Raw water tank: 200L
? Treated water tank: 80L
Flow rates
? Raw water pump: max. 25L/h
? Return sludge pump: max. 25L/h
? Circulation pump: max. 25L/h
Speeds (stirring machines)
? Secondary clarifier: max. 45min-1
? All others: each max. 600min-1
Measuring ranges
? Flow rate:
? 2…25L/h (raw water)
? 50…550L/h (compressed air)
? Temperature: 0…40°C
? pH value: 0…14
? Oxygen concentration: 0…10mg/L
Experiments
- Learning the fundamental principle of the activated sludge process
- Functional principle of nitrification and pre-de-nitrification
- Creation of a stable operating state
- Identification of the following influencing factors
- Return sludge ratio
- Return ratio of the internal recirculation
- Sludge age
- Sludge loading
- Volumetric loading
- Oxygen concentration, pH value, and temperature
- The efficiency of the pre-de-nitrification
Requirements
Mains Power 220 – 240V @ 50Hz, 1Ph









 91-9829132777
91-9829132777