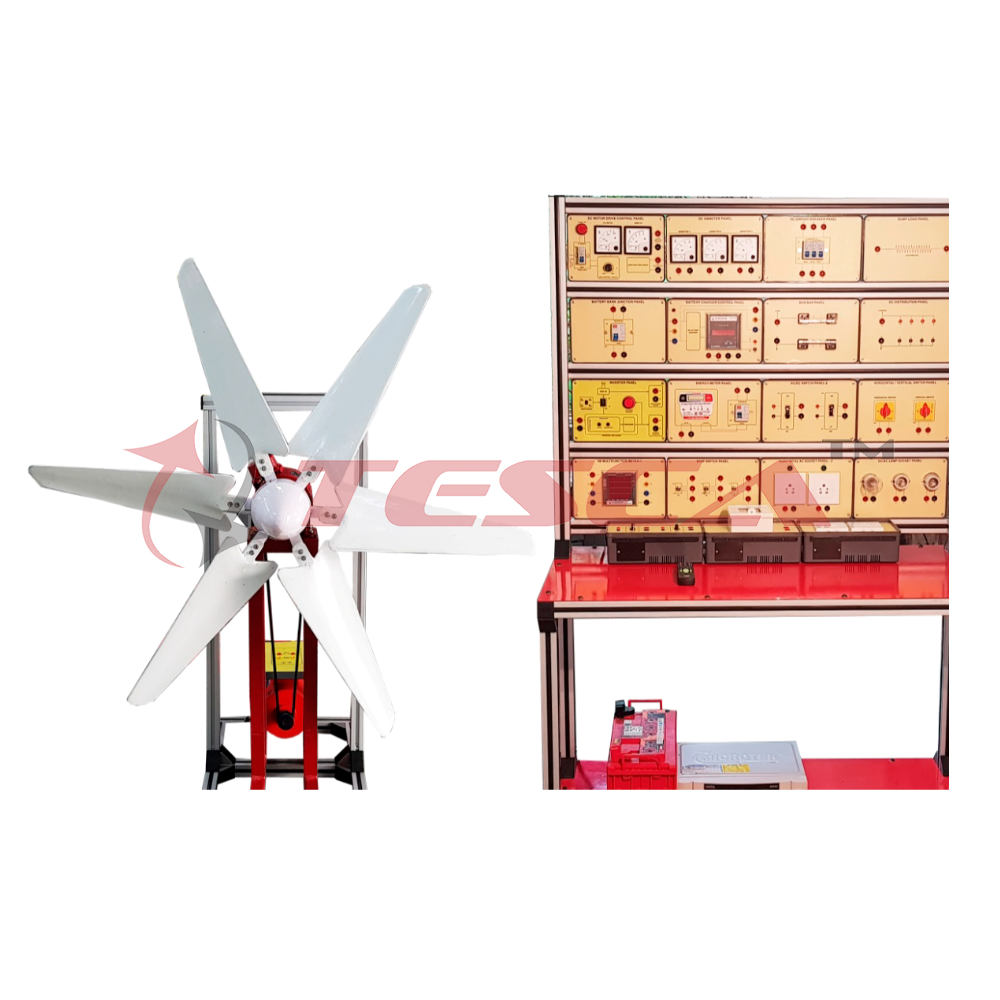
Renewable Wind Energy Trainer

Order Code: 32487
Category: Environmental Trainers
Renewable energies are energy sources that are continuously being replenished by natural processes that occur on human timescales. In contrast, fossil fuels (coal, natural gas, oil) require millions of years of geological processes to form. Our resou...
SPECIFICATION
Renewable energies are energy sources that are continuously being replenished by natural processes that occur on human timescales. In contrast, fossil fuels (coal, natural gas, oil) require millions of years of geological processes to form. Our resources of fossil and nuclear fuels (e.g. uranium) are limited. Regenerative energies, on the other hand, are virtually in exhaustible.
Wind energy is a form of solar energy. Wind energy (or wind power) describes the process by which wind is used to generate electricity. Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy in the wind into mechanical power. A generator can convert mechanical power into electricity. Mechanical power can also be utilized directly for specific tasks such as pumping water.
Wind power is the use of air flow through wind turbines to provide the mechanical power to turn electric generators. Wind power, as an alternative to burning fossil fuels, is plentiful, renewable, widely distributed, clean, produces no greenhouse gas emissions during operation, consumes no water, and uses little land.
The net effects on the environment are far less problematic than those of nonrenewable power sources.
Wind farms consist of many individual wind turbines, which are connected to the electric power transmission network. Onshore wind is an inexpensive source of electric power, competitive with or in many places cheaper than coal or gas plants. Offshore wind is steadier and stronger than on land and offshore farms have less visual impact, but construction and maintenance costs are considerably higher. Small onshore wind farms can feed some energy into the grid or provide electric power to isolated off-grid locations.
Specifications
DC Motor Drive Control panel:
- 2 pole 1Ø 6A MCB of 230 V 50Hz.
- 300V DC Voltmeter & 5A DC Ammeter
- 0-200V Variable Armature Output and Fixed 200V Field Output
DC Ammeter panel:
- 3 No’s of 0-20A DC Ammeter
DC Circuit Breaker panel:
- 3 No’s of 1Ø 16A MCB Circuit Breaker.
Battery Bank Junction Panel:
- 2 pole 1Ø 16A ELCB Switch.
- Dump Load panel:
- 0.5Ω /100W resistive load.
Socket Panel:
- 3 No’s of Screw Base Lamp Socket.
- 2 No’s of 1Ø AC Electrical Socket.
Switch Panel:
- 1 No’s of 16A Cam operated rotary Horizontal Switch.
- 1 No’s of 16A Cam operated rotary Vertical Switch.
- 2 No’s of AC/DC switch.
- 3 No’s of Stop (Toggle) Switch
Bus Bar & Distribution Panel:
- 12V DC bus bar
- 12V DC Distribution bar
Battery Charger Control Panel:
- 3Ø Battery Charger with DC Energy Meter to measure DC parameter of Battery.
3 Phase Multifunction Meter
- 1 No’s. of 3 Phase Multifunction Meter to measure AC voltage, current, power etc
Energy Meter Panel:
- 1Ø AC two wires static kWh Meter with 2 pole 1Ø 16A ELCB Switch.
Inverter Panel:
- 900VA pure sine wave Inverter with AC Output Indicator.
Battery Panel:
- 12V, 100Ah Tubular Battery for storage.
Wind Simulator:
- Wind Simulator with DC Shunt Motor and 3Ø Alternator.
3 Phase Alternator
- Speed-500 RPM
- Capacity-100 VA
- Voltage-12 V
- Current-8 A
- Frame-90









 91-9829132777
91-9829132777